Overview
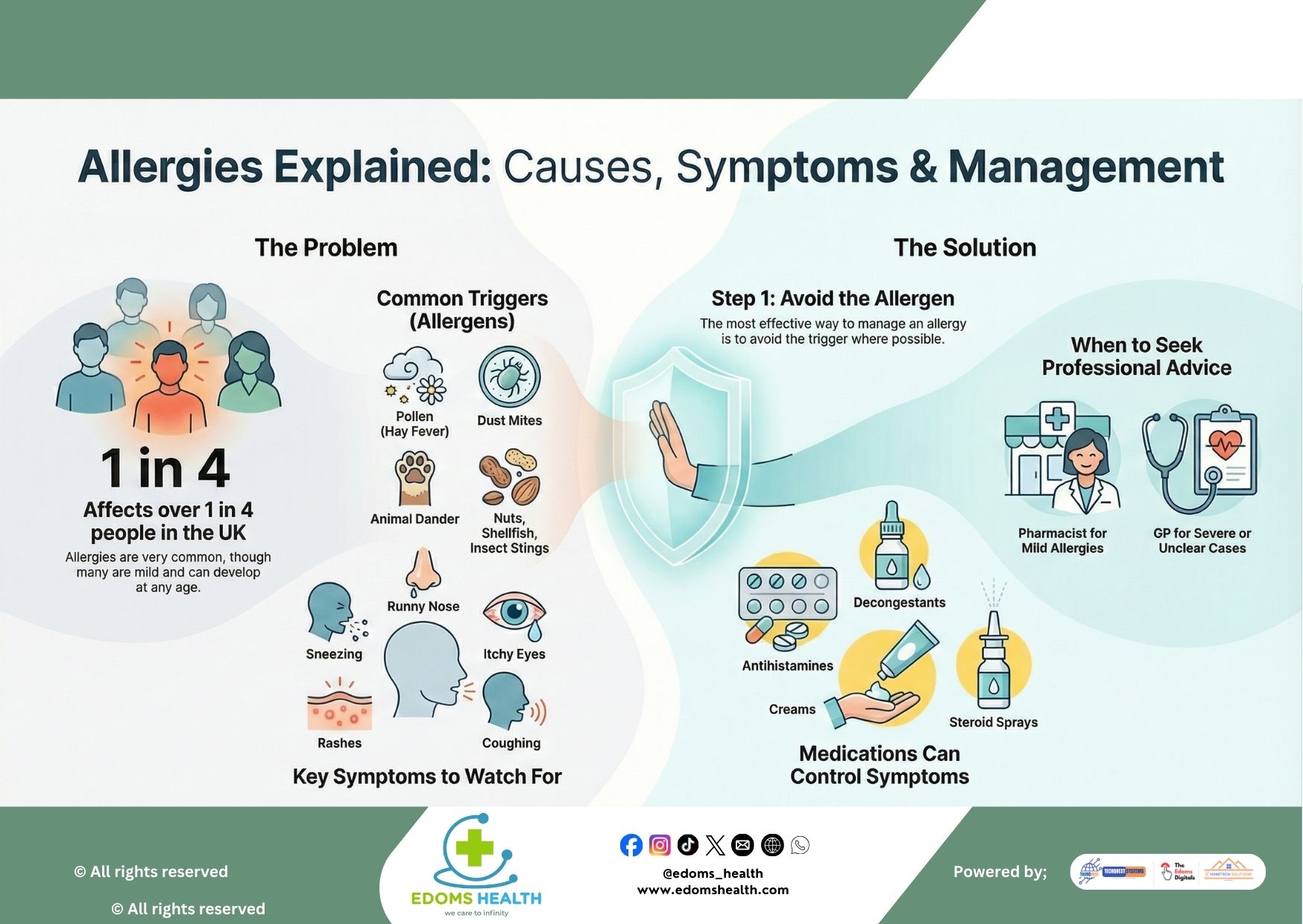
Allergies are more than just a seasonal nuisance—they are a common health issue that impacts the daily lives of millions. In the UK alone, over 1 in 4 people are affected by some form of allergy. While many cases are mild, allergies can develop at any age and vary widely in severity, making understanding and management essential for maintaining quality of life.
What Are Allergies?
An allergy occurs when the body’s immune system reacts to a usually harmless substance as if it were a threat. These substances, known as allergens, can trigger a range of symptoms that affect the skin, respiratory system, eyes, and digestive tract.
Common Allergy Triggers
Allergens are everywhere, and knowing what to look out for can help you take preventive action. Common triggers include:
- Pollen – Causes hay fever, especially in spring and summer.
- Dust Mites – Tiny organisms found in household dust.
- Animal Dander – Skin flakes, saliva, or urine from pets.
- Foods – Such as nuts and shellfish.
- Insect Stings – From bees, wasps, and other insects.
- Medications and Latex – Less common but significant triggers.
Recognising the Symptoms
Allergic reactions can manifest in various ways. Common symptoms include:
- Runny or blocked nose
- Itchy, red, or watery eyes
- Frequent sneezing
- Coughing or wheezing
- Skin rashes, hives, or eczema
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or face
- In severe cases, difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis
Mild symptoms may be mistaken for a common cold, but if they persist or occur in response to specific exposures, an allergy may be the cause.
How to Manage Allergies Effectively
Step 1: Avoid the Allergen
The most effective way to prevent allergic reactions is to avoid known triggers whenever possible. Practical steps include:
- Keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons
- Using allergen-proof bedding to minimise dust mites
- Bathing pets regularly and keeping them out of bedrooms
- Reading food labels carefully and informing restaurants of allergies
- Wearing insect repellent and protective clothing outdoors
Step 2: Use Medications to Control Symptoms
When avoidance isn’t enough, medications can help manage symptoms. Options include:
- Antihistamines – For sneezing, itching, and runny nose
- Nasal Sprays – To reduce nasal congestion and inflammation
- Eye Drops – For itchy or watery eyes
- Inhalers – For asthma-like symptoms triggered by allergies
- Steroid Creams – For eczema and skin reactions
Many of these are available over-the-counter, but stronger formulations may require a prescription.
Step 3: Consider Long-Term Solutions
For persistent or severe allergies, a doctor may recommend:
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots or tablets) – Gradually desensitises the immune system to specific allergens
- Personalised Allergy Action Plans – Especially important for those at risk of severe reactions
When to Seek Professional Help
Not all allergies can be self-managed. It’s important to know when to seek expert advice:
- Consult a Pharmacist – For mild, well-understood allergies. They can recommend treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
- See a GP – If symptoms are severe, unclear, or not improving with over-the-counter treatments. A GP can provide a formal diagnosis, prescribe stronger medications, or refer you to an allergy specialist.
In cases of severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)—such as swelling, breathing difficulties, or collapse—seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Living Well with Allergies
While allergies can be inconvenient and sometimes frightening, they don’t have to control your life. With careful planning, appropriate treatment, and professional guidance, most people with allergies can lead full, active lives. Awareness, prevention, and timely intervention are key to staying safe and comfortable—whatever the season or situation.